Understanding katna¶
As mentioned in intro section katna consists of two modules, Video and Image, In this section we will go into details about each modules working.
Katna.video Module:¶
Video module handles the task(s) for key frame(s) extraction and video compression. This module has four primary public functions for keyframe extraction video_compression, which are extract_video_keyframes, extract_keyframes_from_videos_dir, compress_video and compress_videos_from_dir.
extract_video_keyframes is the primary function which given a video file extracts most important keyframe from a video. extract_keyframes_from_videos_dir actually runs extract_video_frames function for all video files in a directory recursively. Katna.video frame extraction feature first takes a video and divides a big video in smaller chunks of videos, it runs video frame extraction and frame selector tasks on these chunked videos in parallel. For each chunked video actual frame extraction is done in Katna by following two separate modules.
Details about public compress_video and compress_videos_from_dir functions is listed in Katna.video_compressor module.
Katna.frame_extractor module¶
In frame extractor module given a input video all the video frames that are sufficiently different from previous ones using absolute differences in LUV colorspace are returned.
Katna.frame_selector module¶
In Katna.frame_selector module given list of frames returned from frame_extractor module following checks are performed:
- Brightness score filtering of extracted frames.
- Entropy/contrast score filtering of extracted frames.
Each of these properties are filtered based on threshold which you can check and edit in Katna.config.ImageSelector properties.
After frame filtering based on number of required frames N, N clusters are formed using K-Means clustering where K=N, clustering is done using image histogram based approach. After K-Means clustering, for each cluster selection of best frame from cluster is done using variance of laplacian sorting. In image processing world variance of laplacian method is often used for image blur detection. This sorting and selection ensures that least blurred image is selected from cluster.
Katna.video_compressor module¶
Apart from Frame extraction Katna.video module can also do efficient video compression. It is done by internal module called internally by Katna.video_compressor module and exposed publicly by two public functions: compress_video and compress_videos_from_dir As the name suggests compress_video function does video compression on a single input video file and compress_videos_from_dir function recursively compresses all videos in a given input folder. Katna.video_compressor includes actual implementation of video compression using ffmpeg library.
As discussed compress_video functions can compress a given input video and saves the output in same folder with name=original_input_file_name + “_compressed” with mp4 extension. You can change this behavior and other Configurations using optional parameters.
In case you play around with the different parameters like where to save compressed file etc. you can change optional parameters in compress_video function. Below are the optional parameters supported by the method
1. force_overwrite (bool, optional) – optional parameter if True then if there is already a file in output file location function will overwrite it, defaults to False
2. crf_parameter (int, optional) – Constant Rate Factor Parameter for controlling amount of video compression to be applied, The range of the quantizer scale is 0-51: where 0 is lossless, 23 is default, and 51 is worst possible. It is recommend to keep this value between 20 to 30 A lower value is a higher quality, you can change default value by changing config.Video.video_compression_crf_parameter
3. output_video_codec (str, optional) – Type of video codec to choose, Currently supported options are libx264 and libx265, libx264 is default option. libx264 is more widely supported on different operating systems and platforms, libx265 uses more advanced x265 codec and results in better compression and even less output video sizes with same or better quality. Right now libx265 is not as widely compatible on older versions of MacOS and Widows by default. If wider video compatibility is your goal you should use libx264., you can change default value by changing Katna.config.Video.video_compression_codec
4. out_dir_path (str, optional) – output folder path where you want output video to be saved, defaults to “”
5. out_file_name (str, optional) – output filename, if not mentioned it will be same as input filename, defaults to “”
Katna.video_resize module¶
As mentioned in home section since version 0.8.0 of Katna we are extending smart resize features to videos with the help of Google’s Mediapipe project. In simple terms video resize functionality in Katna currently is a thin python wrapper around Google Mediapipe Autoflip solution. If you want to learn more about how it works under the hood Please refer to this blog post by Google AI: https://ai.googleblog.com/2020/02/autoflip-open-source-framework-for.html . Please refer to Smart video resize using katna for how to install and configure mediapipe to be used with katna. Right now following parameters are configurable using Katna video module:
- STABALIZATION_THRESHOLD (float, optional) – defaults to “0.5” : This parameter controls extent of motion stabilization is applied while tracking an object or face across the frames for video resizing. Higher value Means more aggressive motion stabilization and vice versa.
- BLUR_AREA_OPACITY (int, optional) – defaults to “0.6” In some cases e.g. while compulsorily including all faces across frames, it is not possible to do without rendering padding in video. In case overlay of same video content is used as padding. This parameter controls how much opacity to add to padded content.
- ENFORCE_FEATURES.FACE_CORE_LANDMARKS (bool, optional) – defaults to False In case of this parameter set as true, It is ensured that all face present in video are compulsorily included in final resized video.
- ENFORCE_FEATURES.FACE_FULL (bool, optional) – defaults to False In case of this parameter set as true, It is ensured that all full faces present in video are compulsorily included in final resized video.
- ENFORCE_FEATURES.HUMAN (bool, optional) – defaults to False In case of this parameter set as true, It is ensured that all persons/humans present/detected in video are compulsorily included in final resized video.
- ENFORCE_FEATURES.PET (bool, optional) – defaults to False In case of this parameter set as true, It is ensured that all PET’s like dogs and cats present/detected in video are compulsorily included in final resized video.
- ENFORCE_FEATURES.CAR (bool, optional) – defaults to False In case of this parameter set as true, It is ensured that all CARs present/detected in video are compulsorily included in final resized video.
- ENFORCE_FEATURES.OBJECT (bool, optional) – defaults to False In case of this parameter set as true, It is ensured that all objects detected in video are compulsorily included in final resized video.
Mediapipe Autoflip Integration¶
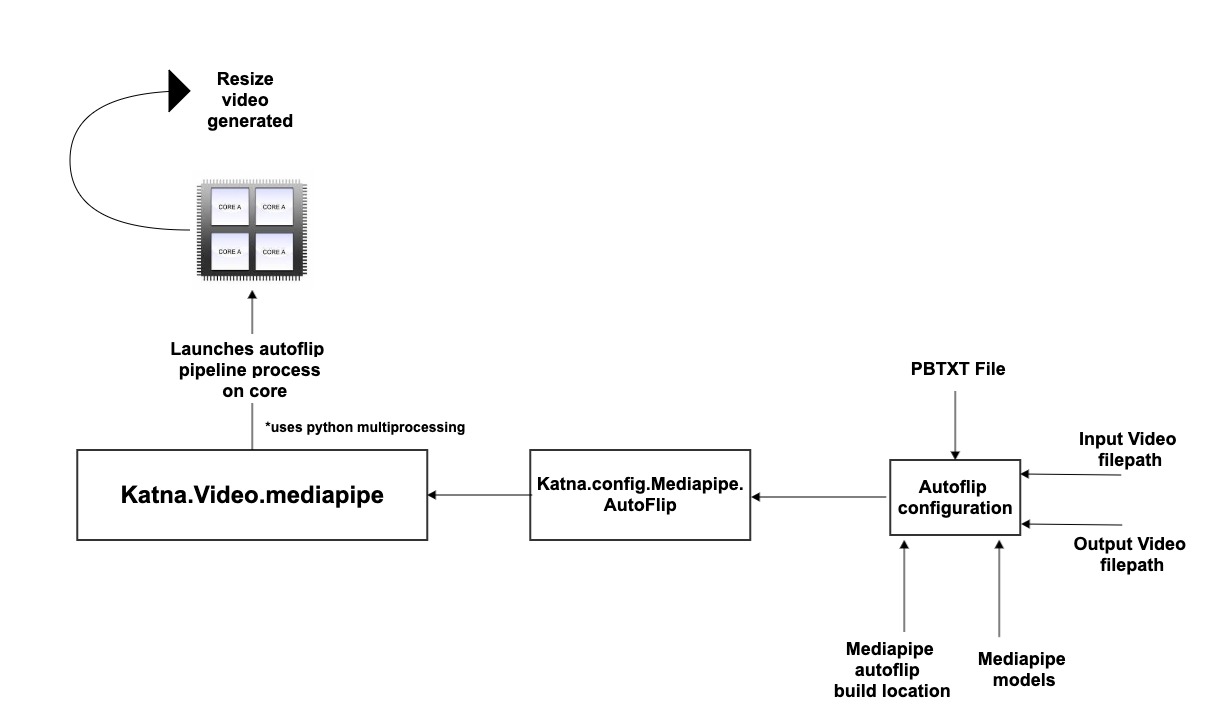
Katna uses python multiprocessing to create a pool of processes based on the number of cpu cores on machine, and launch processes to resize video on these cores. For example on a 12 core machine, if 4 videos needs to be resized in parallel, Katna will launch mediapipe autoflip pipeline for 4 videos on 4 cores.
Since mediapipe is installed outside of Katna, mediaipie autoflip pipeline is launched using the python subprocess module. To ensure smooth run, Katna needs build autorun directory path (where binaries are build) and also the mediapipe models directory which containe tflite (tensorflow lite models for CPU). Internally, Katna creates a simlink to the models folder directory during its instance of execution. This allow Katna to access the models file required to run autoflip pipeline.
Below you can see a simple architecture describing the integration:
Katna provides an interface to configure autoflip. This enables Katna to hide the complexity of autoflip graphs configuration (.pbtxt file) and provide users will relevant configurations in the form of python friendly dictionary. Behind the scenes, Katna will create a temporary graph (.pbtxt) file based on the configuration provided and use it to run the autoflip pipeline.
Katna users can check temp_pbtxt directory when the pipeline is running to look at the mediapipe autoflip graph file. The folders gets deleted automatically when the pipeline finishes its execution.
To check the list of configurable options, check Katna.video_resize module.
Katna.image Module:¶
This module handles the task(s) for smart cropping. The Smart crop feature tries to automatically identify important image areas where the user will focus more and tries to retain it while cropping. For a given input cropping dimension/final output image size, Katna.image works by first extracting all possible image crop given crop specification using katna.crop_extractor module, Katna.crop_selector module then uses various filtering and selection criteria to select best crops from list of image crops. Let’s read more about these two modules in details.
Katna.crop_extractor module¶
Katna.crop_extractor module works by given a crop specification using a sliding window approach it first calculates all possible crop see _get_all_possible_crops() function inside Katna.crop_extractor module. Additionally it applies rule of third and crop rectangle distance from edge score. Configurations related to these scoring rules could be edited in Katna.config.CropScorer module.
Katna.crop_selector module¶
After returning candidate crops from crop_extractor module Katna.crop_selector module first does further filtering using Katna.image_filters filters. At the moment only text filter is supported. Text filter ensures that if cropped rectangle contains text, texts present is not abruptly cropped.
After performing crop_filtering crop selection is done by first calculating additional crop scoring is done based on following criteria: Saliency, edge features and Face features. This score is then combined with rule of third and crop distance from edge feature calculated in crop_extractor module. Configurations related to these scoring rules could be edited in Katna.config.CropScorer, Katna.config.EdgeFeature, Katna.config.FaceFeature modules.